Abstract:
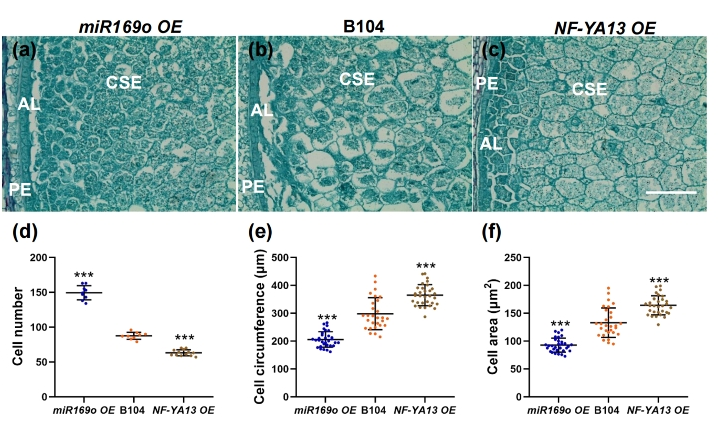
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play key regulatory rolesinseeddevelopment and emerge as new key targets for engineering grainsizeand yield.TheZma-miRNA169 family is highly expressed duringmaizeseeddevelopment, but its functional rolesinseeddevelopment remain elusive. Here, we generated zma-miR169oandZmNF-YA13transgenic plants. Phenotypic and genetic analyses were performed on these lines.Seeddevelopment and auxins contents were investigated. OverexpressionofmaizemiRNA zma-miR169oincreasesseedsizeandweight, whereastheopposite is true when itsexpressionis suppressed. Further studies revealedthatzma-miR169 acts by negatively regulating its target gene, a transcription factorZmNF-YA13thatalso plays a key roleindeterminingseedsize. We demonstratethatZmNF-YA13regulatestheexpressionoftheauxin biosynthetic geneZmYUC1, which modulates auxin levelsintheearly developing seeds anddeterminesthenumberofendosperm cells, thereby governingmaizeseedsizeand ultimately yield. Overall, our present study has identified zma-miR169oandZmNF-YA13thatform a functional module regulating auxin accumulationinmaizeseeds and playing an important roleindeterminingmaizeseedsizeand yield, providing a setofnovel molecular tools for yield improvementinmolecular breeding and genetic engineering.
Keywords:auxin、endosperm、kernelsize、maize、zma-miR169、ZmNF-YA13、ZmYUC1