Recently, the Microbial Intelligent Design and Synthesis Innovation Team of the Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, proposed a new proteindissection strategy based on "splitting unit pairs". By dividinglarge enzyme into “splitting units” and combinatorial biosynthesis in heterologous hosts, the insecticidal nonribosomal peptides (NRPs) can be synthesized efficiently. The dissection strategy accelerates the development and modification of biopesticide molecules. Relevant research results were published in the internationally authoritative journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
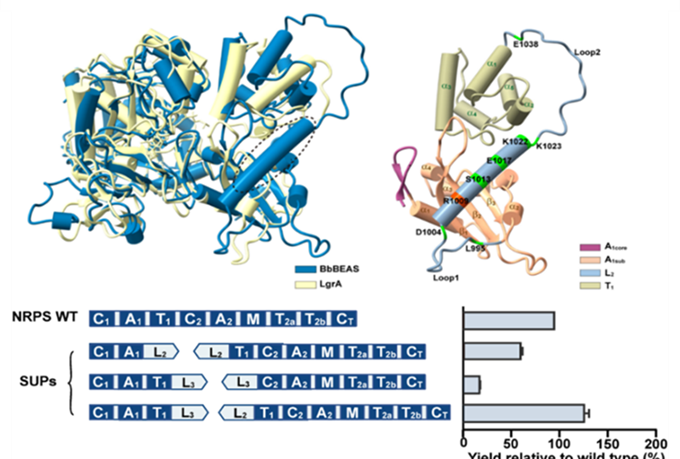
The enzymesare responsible for the biosynthesis of small agricultural insecticidal molecules such as beauvericin and destruxins, aremultifunctional megaenzymes.However, the extremely large size and complexity of the enzymes pose formidable challenges to the production of such nonribosomal peptides by combinatorial biosynthesis and synthetic biology. Here we report a new enzyme dissection strategy based on the “Splitting Unit Pairs” (SUPs). This strategy divides enzymes into “splitting units”, each forming an enzyme subunit that contains catalytically independent modules. Functional collaboration between the subunits is then facilitated by artificially thiolation domain duplicating.We successfully achieved the efficient biosynthesis of fungal nonribosomal peptides and their analogues, solved theproblemof re-engineering the macromolecular biopesticides, significantly improved the yield, and synthesized novel biopesticide peptide molecules. This study promoted the development of combinatorial biosynthesis technology, and provided new options for the efficient and rational engineering of nonribosomal peptide biopesticidesproduction.
Researcher Yuquan Xu, Professor István Molnár and postdoctoral fellow Linan Xie are the co-corresponding authors. PhD student Miaomiao Yin and postdoctoral fellow Linan Xie are the co-first authors. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, as well as other fund projects.
|