Recently, Team of Intelligent Design and Biosynthesis of Agro-microbes of the Biotechnology Research InstituteofCAAS, in collaboration with a team from Shanghai Jiaotong University, has systematically analyze the progress of research on the structure and expression strength prediction of artificial promoters in plants, proposed strategies and application pathways for artificial promoter design, and looked forward to the application of artificial promoters in crop breeding. The paper was published in Plant Communication, an internationally renowned journal.
Promoters are important elements for controlling gene expression in plants, mainly by combining different transcription factors to achieve gene expression switches and intensity changes. In recent years, with the development of high-throughput technologies and the application of artificial intelligence in biology, the artificial design of "smart" promoters with multiple features such as "fine, induced expression and tissue specificity" has become a hot topic of research in synthetic biology. The study of avoiding energy dissipation and gene silencing in constitutive promoters has also attracted much attention from the scientific community.
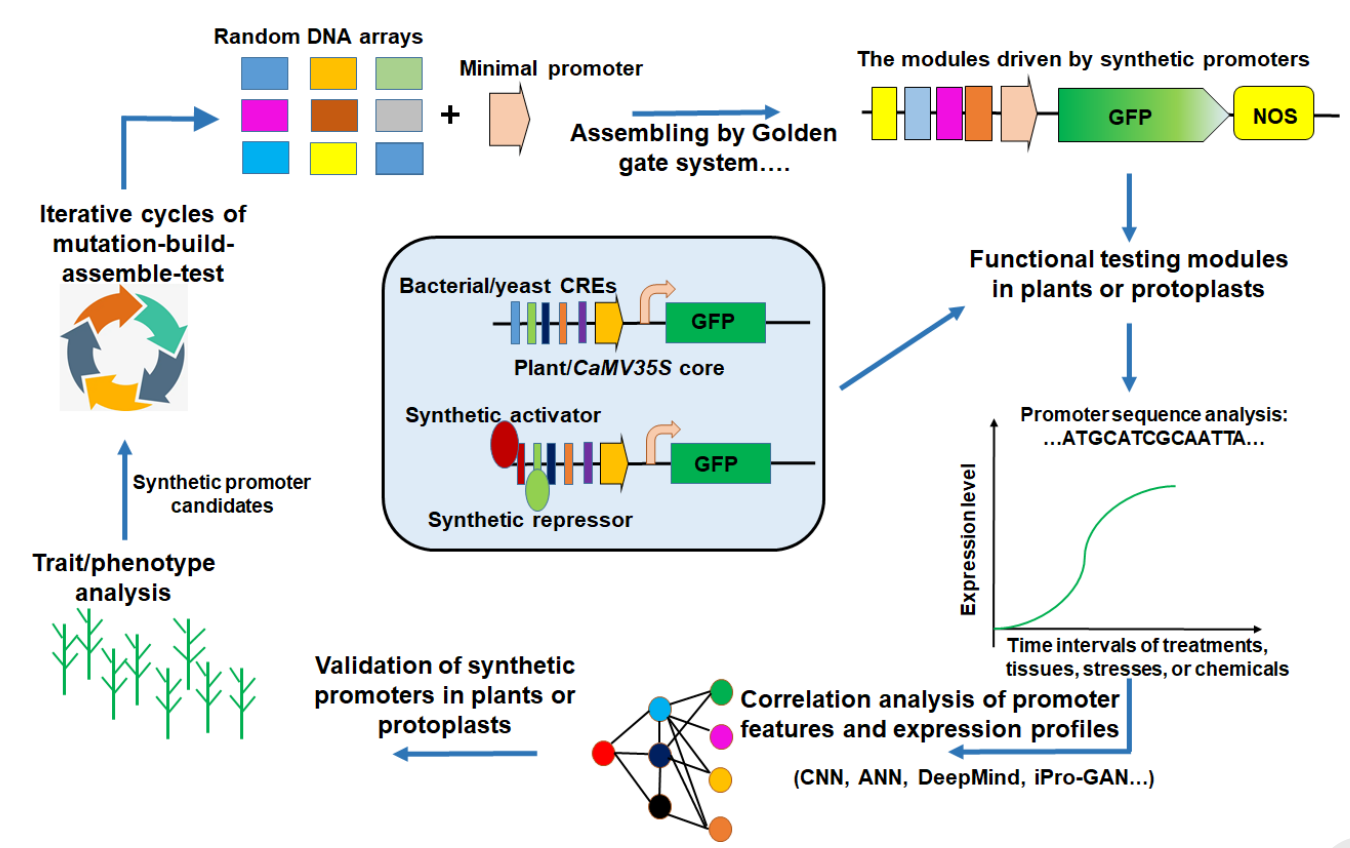
The paper summarizes the progress of research on promoter structure and expression intensity prediction. It was found that the main regulatory interval of most genes is in the -200 to +51 bp region, which controls more than 90% of gene expression intensity, and this is one of the key targets for artificial promoter design. The paper also proposes current pathways for artificial promoter design: one is the minimal promoter strategy. This strategy involves the random synthesis of oligonucleotides or the construction of different cis-element combinations, which are then linked to a Mini 35S or core promoter to drive the expression of the reporter gene. By sequencing the promoters and analyzing the expression of the reporter genes, large amounts of data can be obtained for AI analysis. Based on this, models are constructed to predict promoter strength and guide the design of artificial promoters. Secondly, the promoter directed evolution strategy. This strategy is based on the natural promoters present in plant cells, and different artificial promoters are constructed in plants through saturating artificial mutations generated by gene editing. Candidate germplasm material in breeding is identified through field phenotypic analysis of plants carrying the artificial promoters. This approach has been widely used in crop breeding for disease resistance, strain and yield.
Artificial minimum promoter creation strategy
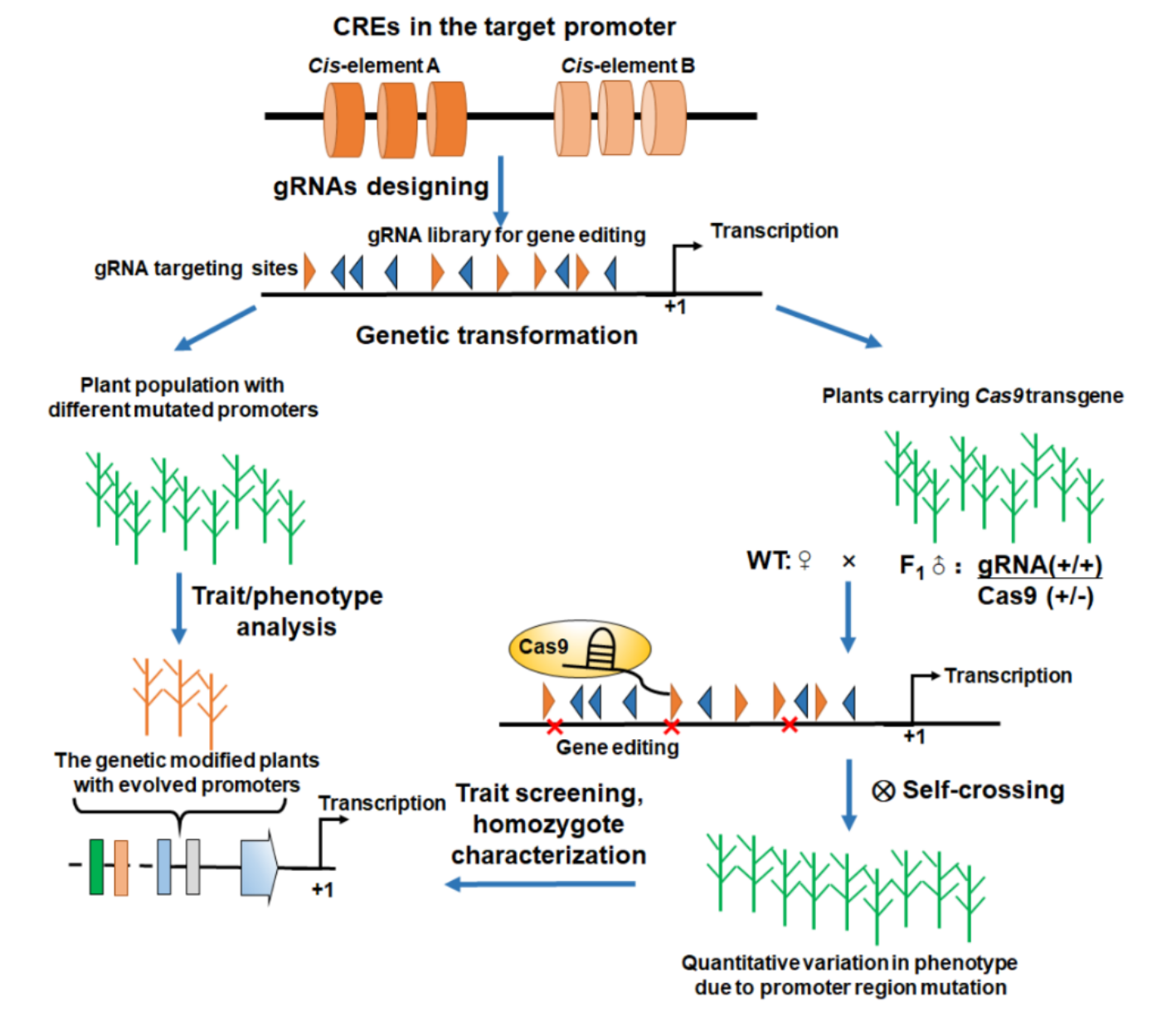
Strategy for promoter-directed evolution
The paper also provides further insights into the trends in artificial promoter design: firstly, the design of tissue-specific expression promoters; secondly, the use of artificial promoter properties as conditional response switches for effective use in gene editing and artificial sensors; and thirdly, the design and use of closed lines controlled by artificial promoters. As artificial intelligence and gene function regulatory networks are further revealed and refined, these different directions will be rapidly applied and yield good results in crop breeding and plant biotechnology.
The research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China for Synthetic Biology, the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guide to Future Biotechnology Guidance Category and the Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. ERUM, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and researcher Jin Wang, Biotechnology Research InstituteofCAAS, are co-first authors. |