Recently, the research group of Prof. RongfengHuang from Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Scienceshas dissected themolecular mechanism of the coordination of ethylene and GA during rice root development, which provides new insightsinto rice root improvement.The results are published on The Plant Cell with the title of “Orchestration of ethylene and gibberellin signals determines primary root elongation in rice”.
As an important belowground plant ground organ, the root system mediates water and nutrient uptake and provides mechanical support for shoot growth, therefore, root development strongly affects plant growth and productivity. Rice is an importantstaple food for more than half of the world population, identification of key regulators of root growth and development could accelerate the cultivation of new rice varieties with high yield and ensure food security.
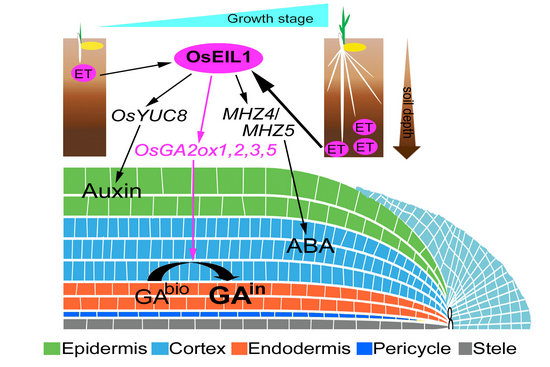
Ethylene is an important gaseous plant hormone that regulates root growth and development. Analysis of the molecular mechanism of ethylene regulating rice root development can promote the process of high-yield molecular breeding of rice.In the present study, we reported that the ethylene signaling transcription factor OsEIL1 promotes the expression of the GA metabolism genes OsGA2ox1, OsGA2ox2, OsGA2ox3, and OsGA2ox5, resulting in the deactivation of GA, which further inhibits cell proliferation in root meristems, and the cessation of primary root growth. Our results shed light on the molecular mechanism of ethylene action during primary root elongation in young rice seedlings, providing insight into the coordination of ethylene and GA during root development and seedling establishment.
This work was funded by National Key R&D Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
|