Abstract:
Waste oil pollution and the treatment of oily waste present a challenge, and the exploitationof microbial resources is a safe and efficient method to resolve these problems. Lipase-producing microorganismscan directly degrade waste oil and promote the degradation of oily waste and, therefore,have very significant research and application value. The isolation of efficient oil-degrading strainsis of great practical significance in research into microbial remediation in oil-contaminated environmentsand for the enrichment of the microbial lipase resource library. In this study, Acinetobacter juniiWCO-9, an efficient oil-degrading bacterium, was isolated from an oil-contaminated soil using oliveoil as the sole carbon source, and its enzyme activity of _-nitrophenyl decanoate (_-NPD) decompositionwas 3000 U/L. The WCO-9 strain could degrade a variety of edible oils, and its degradation capability was significantly better than that of the control strain, A junii ATCC 17908. Comparativepan-genome and lipid degradation pathway analyses indicated that A. junii isolated from thesame environment shared a similar set of core genes and that the species accumulated more specificgenes that facilitated resistance to environmental stresses under different environmental conditions.WCO-9 has accumulated a complete set of oil metabolism genes under a long-term oil-contaminationenvironment, and the compact arrangement of abundant lipase and lipase chaperones has furtherstrengthened the ability of the strain to survive in such environments. This is the main reason whyWCO-9 is able to degrade oil significantly more effectively than ATCC 17908. In addition, WCO-9 possesses a specific lipase that is not found in homologous strains. In summary, A. junii WCO-9,with a complete triglyceride degradation pathway and the specific lipase gene, has great potential inenvironmental remediation and lipase for industry.
KeyWords:
Acinetobacter junii WCO-9; lipase; oil degradation capabilities; pan-genome analysis;
triglyceride degradation pathway
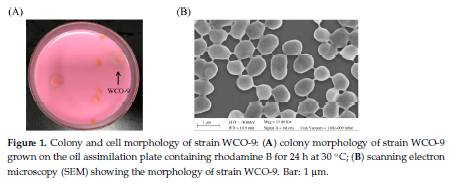

|