Abstract:
Maize is a major staple crop widely used as food, animal feed, and raw materials in industrial production. High-density planting is a major factor contributing to the continuous increase of maize yield. However, high planting density usually triggers a shade avoidance response and causes increased plant height and ear height, resulting in lodging and yield loss. Reduced plant height and ear height, more erect leaf angle, reduced tassel branch number, earlier flowering,and strong root system architecture are five key morphological traits required for maize adaption to high-density planting. In this review, we summarize recent advances in deciphering the genetic and molecular mechanisms of maize involved in response to high-density planting. We also discuss some strategies for breeding advanced maize cultivars with superior performance under high-density planting conditions.
KeyWords:
maize; high-density planting; plant architecture; plant height/ear height; leaf angle; tassel branch; flowering time; root architecture
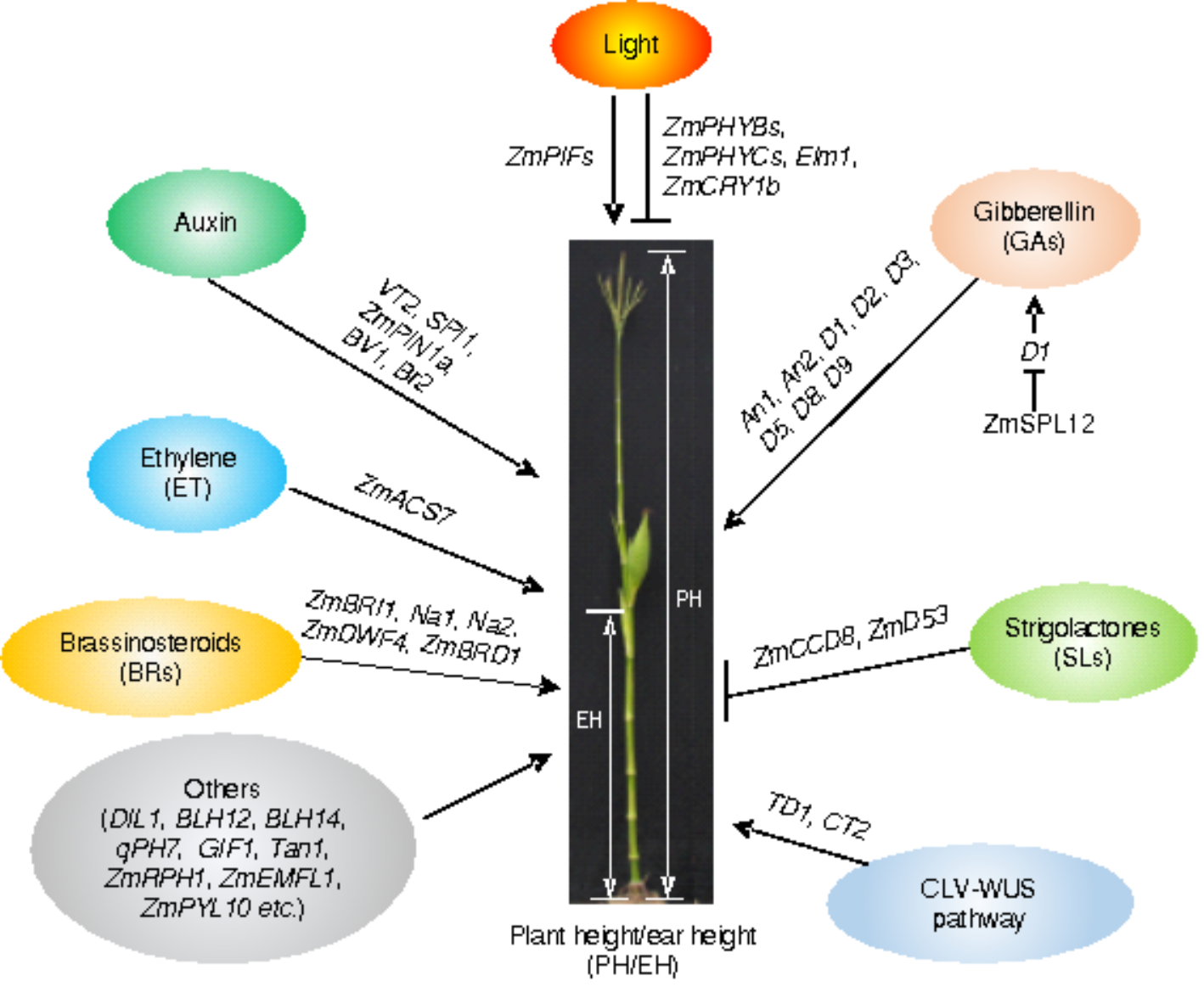
Genetic pathways regulating plant height and ear height in maize
|