Abstract:
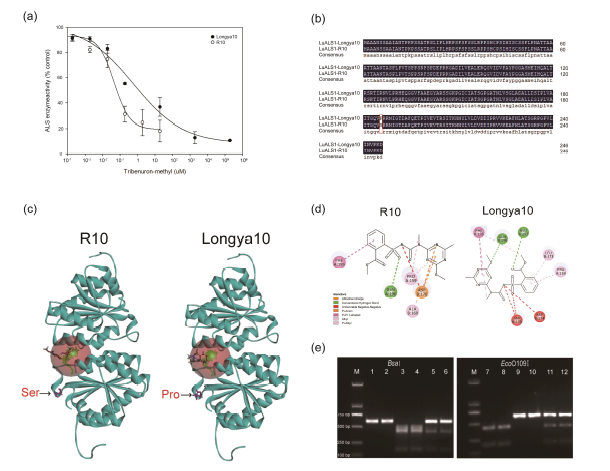
The cultivation of herbicide-resistant crops is an effective tool for weed management in agriculture.Weed control in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) remains challenging due to the lack of availableherbicide-resistant cultivars. In this study, a mutant resistant to acetolactate synthase (ALS)-inhibitingherbicides was obtained by ethyl methanesulphonate (EMS) mutagenesis using an elite cultivar,Longya10. Whole-plant dose–response assays revealed that, compared to Longya10, the mutantwas 11.57-fold more resistant to tribenuron-methyl (TBM) and slightly resistant to imazethapyr(resistance index (mutant/Longya10) < 3). In vitro acetolactate synthase assays showed that therelative resistance of the mutant was 12.63 times more than that of Longya10. A biochemical analysisindicated that there was a Pro197Ser (relative to the Arabidopsis thaliana ALS sequence) substitution within the LuALS1, conferring high resistance to sulfonylurea herbicides in the mutant. dditionally,two cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers, BsaI-LuALS1 and EcoO109I-LuALS1,were developed based on the mutation site for marker assistant selection in breeding. Moreover,the mutant did not cause losses in natural field conditions. We find a mutant with ALS-inhibitingherbicide resistance chemically induced by EMS mutagenesis, providing a valuable germplasm forbreeding herbicide-resistant flax varieties.
KeyWords:
acetolactate synthase; herbicide resistance; flax; mutant

|